Planetary Defense on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Asteroid impact avoidance comprises the methods by which
Asteroid impact avoidance comprises the methods by which

 According to expert testimony in the
According to expert testimony in the
''The Spaceguard Survey: Report of the NASA International Near-Earth-Object Detection Workshop''
,

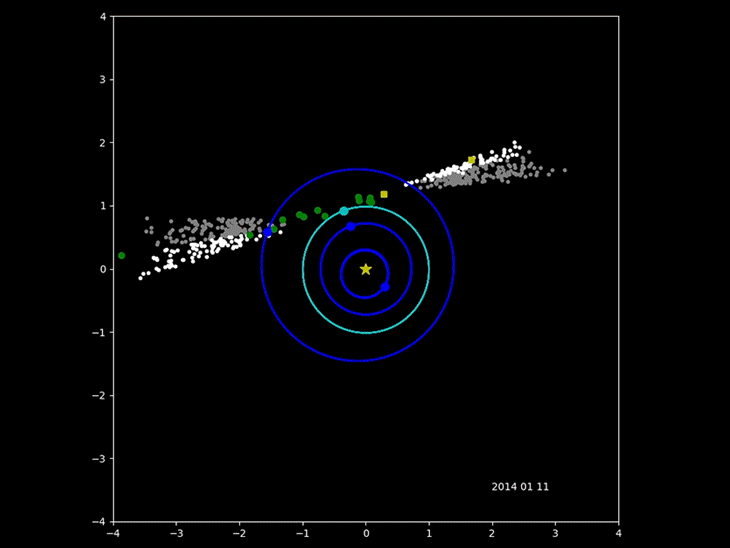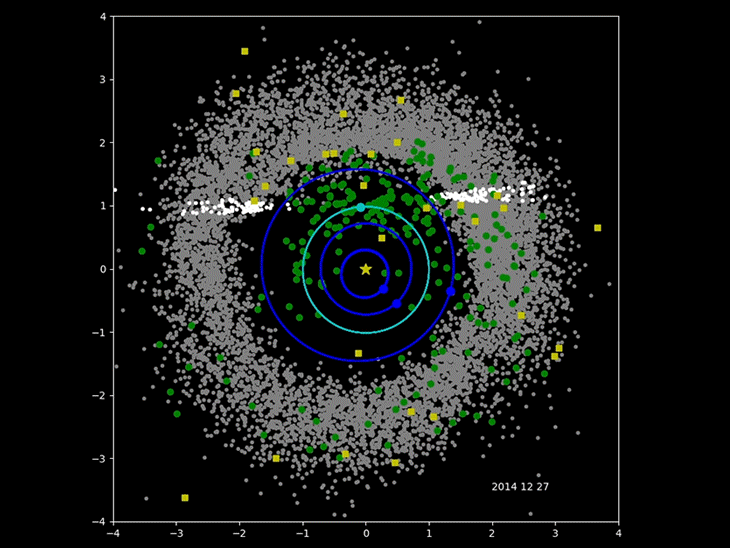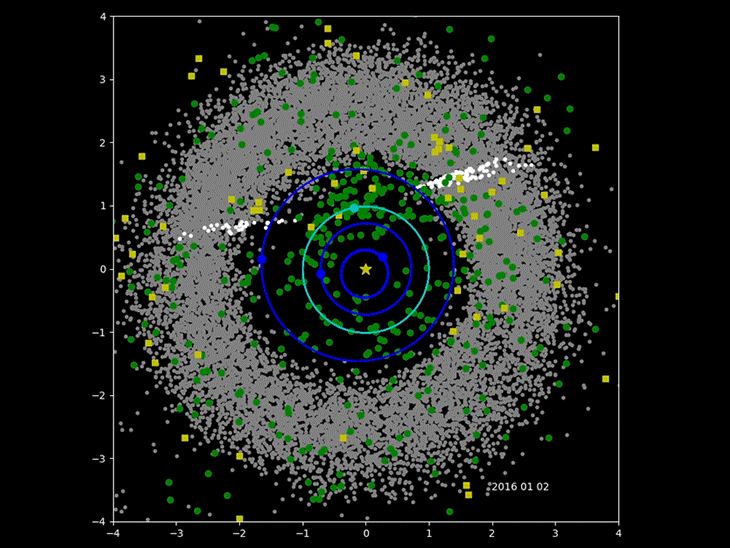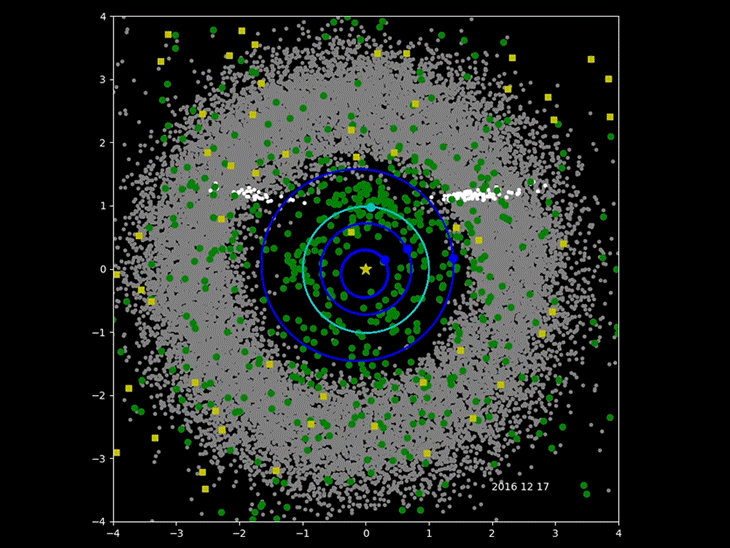 The Minor Planet Center in
The Minor Planet Center in
"Developing Early Warning Systems for Killer Asteroids"
, ''
Vindication for Entrepreneurs Watching Sky: Yes, It Can Fall
, ''
How to Deflect a Killer Asteroid: Researchers Come Up With Contingency Plans That Could Help Our Planet Dodge A Cosmic Bullet
, ''
If an asteroid breaks into fragments, any fragment larger than 35 meters across would not burn up in the atmosphere and itself could impact Earth. Tracking the thousands of
 Initiating a nuclear explosive device proximity fuze, above, impact fuze, on, or slightly Robust Nuclear Earth Penetrator, beneath, the surface of a threatening celestial body is a potential deflection option, with the optimal detonation height dependent upon the composition and size of the object. It does not require the entire NEO to be vaporized to mitigate an impact threat. In the case of an inbound threat from a "rubble pile," the proximity fuze, stand off, or detonation height above the surface configuration, has been put forth as a means to prevent the potential fracturing of the rubble pile. The energetic neutrons and soft X-rays released by the detonation, which do not appreciably penetrate matter, are converted into heat upon encountering the object's surface matter, radiation implosion, ablatively vaporizing all Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight exposed surface areas of the object to a shallow depth, turning the surface material it heats up into ejecta, and, analogous to the ejecta from a chemical rocket engine exhaust, changing the velocity, or "nudging", the object off course by the reaction, following Newton's third law, with ejecta going one way and the object being propelled in the other.
Initiating a nuclear explosive device proximity fuze, above, impact fuze, on, or slightly Robust Nuclear Earth Penetrator, beneath, the surface of a threatening celestial body is a potential deflection option, with the optimal detonation height dependent upon the composition and size of the object. It does not require the entire NEO to be vaporized to mitigate an impact threat. In the case of an inbound threat from a "rubble pile," the proximity fuze, stand off, or detonation height above the surface configuration, has been put forth as a means to prevent the potential fracturing of the rubble pile. The energetic neutrons and soft X-rays released by the detonation, which do not appreciably penetrate matter, are converted into heat upon encountering the object's surface matter, radiation implosion, ablatively vaporizing all Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight exposed surface areas of the object to a shallow depth, turning the surface material it heats up into ejecta, and, analogous to the ejecta from a chemical rocket engine exhaust, changing the velocity, or "nudging", the object off course by the reaction, following Newton's third law, with ejecta going one way and the object being propelled in the other.
Depending on the energy of the explosive device, the resulting reaction engine, rocket exhaust effect, created by the high velocity of the asteroid's vaporized mass ejecta, coupled with the object's small reduction in mass, would produce enough of a change in the object's orbit to make it miss the Earth. A Hypervelocity Asteroid Mitigation Mission for Emergency Response (HAMMER) has been proposed.
, ''Time (magazine), Time'', June 16, 1967.Day, Dwayne A.
"Giant bombs on giant rockets: Project Icarus"
, ''The Space Review'', Monday, July 5, 2004 The design study was later published as 1566 Icarus#Project Icarus, Project IcarusKleiman Louis A.
''Project Icarus: an MIT Student Project in Systems Engineering''
, Cambridge, Massachusetts : MIT Press, 1968 which served as the inspiration for the 1979 film ''Meteor (film), Meteor''."MIT Course precept for movie"
, ''The Tech'', MIT, October 30, 1979 A
These effectiveness figures are considered to be "conservative" by its authors, and only the thermal X-ray output of the B83 devices was considered, while neutron heating was neglected for ease of calculation purposes.
 In 2011, the director of the Asteroid Deflection Research Center at Iowa State University, Dr. Bong Wie (who had published kinetic impactor deflection studies previously), began to study strategies that could deal with objects when the time to Earth impact was less than one year. He concluded that to provide the required energy, a nuclear explosion or other event that could deliver the same power, are the only methods that can work against a very large asteroid within these time constraints.
This work resulted in the creation of a conceptual Hypervelocity Asteroid Intercept Vehicle (HAIV), which combines a Deep Impact (spacecraft), kinetic impactor to create an initial Impact crater, crater for a follow-up subsurface nuclear detonation within that initial crater, which would generate a high degree of efficiency in the conversion of the nuclear energy that is released in the detonation into propulsion energy to the asteroid.
A similar proposal would use a surface-detonating nuclear device in place of the kinetic impactor to create the initial crater, then using the crater as a rocket nozzle to channel succeeding nuclear detonations.
At the 2014 NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) conference, Wie and his colleagues stated that "we have the solution, using our baseline concept, to be able to mitigate the asteroid-impact threat, with any range of warning." For example, according to their computer models, with a warning time of 30 days, a asteroid would be neutralized by using a single HAIV, with less than 0.1% of the destroyed object's mass potentially striking Earth, which by comparison would be more than acceptable.
As of 2015, Wie has collaborated with the Danish Emergency Asteroid Defence Project (EADP), which ultimately intends to crowdsource sufficient funds to design, build, and store a non-nuclear HAIV spacecraft as planetary insurance. For threatening asteroids too large and/or too close to Earth impact to effectively be deflected by the non-nuclear HAIV approach, nuclear explosive devices (with 5% of the explosive yield than those used for the stand-off strategy) are intended to be swapped in, under international oversight, when conditions arise that necessitate it.
In 2011, the director of the Asteroid Deflection Research Center at Iowa State University, Dr. Bong Wie (who had published kinetic impactor deflection studies previously), began to study strategies that could deal with objects when the time to Earth impact was less than one year. He concluded that to provide the required energy, a nuclear explosion or other event that could deliver the same power, are the only methods that can work against a very large asteroid within these time constraints.
This work resulted in the creation of a conceptual Hypervelocity Asteroid Intercept Vehicle (HAIV), which combines a Deep Impact (spacecraft), kinetic impactor to create an initial Impact crater, crater for a follow-up subsurface nuclear detonation within that initial crater, which would generate a high degree of efficiency in the conversion of the nuclear energy that is released in the detonation into propulsion energy to the asteroid.
A similar proposal would use a surface-detonating nuclear device in place of the kinetic impactor to create the initial crater, then using the crater as a rocket nozzle to channel succeeding nuclear detonations.
At the 2014 NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) conference, Wie and his colleagues stated that "we have the solution, using our baseline concept, to be able to mitigate the asteroid-impact threat, with any range of warning." For example, according to their computer models, with a warning time of 30 days, a asteroid would be neutralized by using a single HAIV, with less than 0.1% of the destroyed object's mass potentially striking Earth, which by comparison would be more than acceptable.
As of 2015, Wie has collaborated with the Danish Emergency Asteroid Defence Project (EADP), which ultimately intends to crowdsource sufficient funds to design, build, and store a non-nuclear HAIV spacecraft as planetary insurance. For threatening asteroids too large and/or too close to Earth impact to effectively be deflected by the non-nuclear HAIV approach, nuclear explosive devices (with 5% of the explosive yield than those used for the stand-off strategy) are intended to be swapped in, under international oversight, when conditions arise that necessitate it.
 Following the 1994 Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet impacts with Jupiter, Edward Teller proposed, to a collective of U.S. and Russian ex-Cold War weapons designers in a 1995 planetary defense workshop meeting at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), that they collaborate to design a Nuclear weapon design#Arbitrarily large multi-staged devices, one-gigaton nuclear explosive device, which would be equivalent to the kinetic energy of a asteroid.Planetary defense workshop LLNL 1995
Following the 1994 Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet impacts with Jupiter, Edward Teller proposed, to a collective of U.S. and Russian ex-Cold War weapons designers in a 1995 planetary defense workshop meeting at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), that they collaborate to design a Nuclear weapon design#Arbitrarily large multi-staged devices, one-gigaton nuclear explosive device, which would be equivalent to the kinetic energy of a asteroid.Planetary defense workshop LLNL 1995
/ref>A new use for nuclear weapons: hunting rogue asteroids A persistent campaign by weapons designers to develop a nuclear defense against extraterrestrial rocks slowly wins government support 2013
The theoretical one-gigaton device would weigh about 25–30 tons, light enough to be lifted on the Energia (rocket), Energia rocket. It could be used to instantaneously vaporize a asteroid, divert the paths of Global catastrophic risk, ELE-class asteroids (greater than in diameter) within short notice of a few months. With one year of notice, and at an interception location no closer than Jupiter, it could also deal with the even rarer List of periodic comets, short period comets that can come out of the Kuiper belt and transit past Earth orbit within two years. For comets of this class, with a maximum estimated diameter of , 2060 Chiron, Chiron served as the hypothetical threat. In 2013, the related National Laboratories of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, US and Rosatom, Russia signed a deal that includes an intent to cooperate on defense from asteroids.
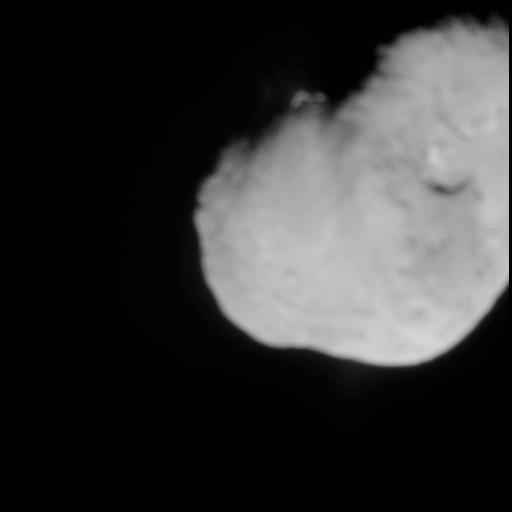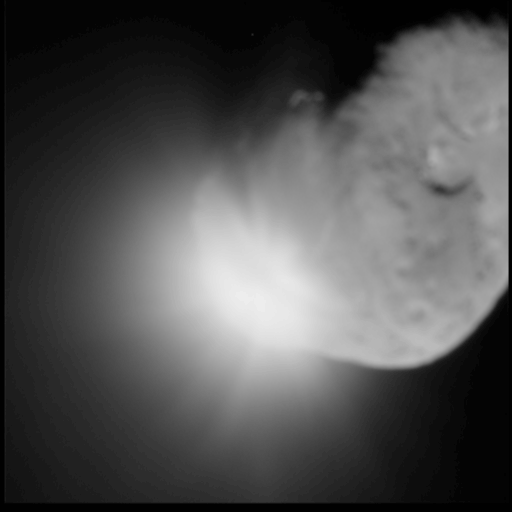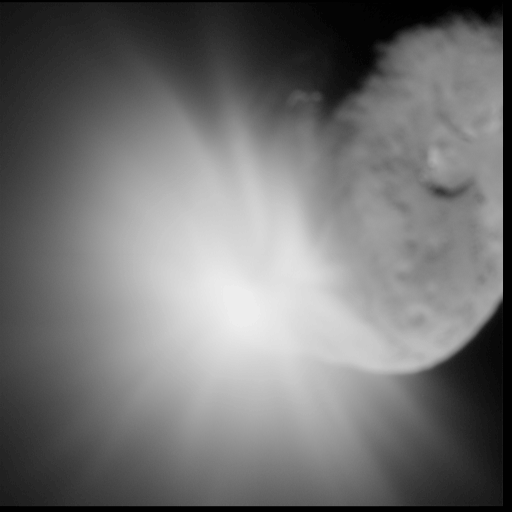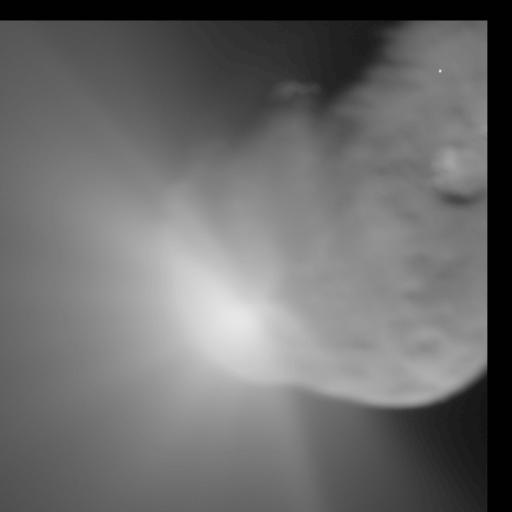 The impact of a massive object, such as a spacecraft or even another near-Earth object, is another possible solution to a pending NEO impact. An object with a high mass close to the Earth could be sent out into a collision course with the asteroid, knocking it off course.
When the asteroid is still far from the Earth, a means of deflecting the asteroid is to directly alter its momentum by colliding a spacecraft with the asteroid.
A
The impact of a massive object, such as a spacecraft or even another near-Earth object, is another possible solution to a pending NEO impact. An object with a high mass close to the Earth could be sent out into a collision course with the asteroid, knocking it off course.
When the asteroid is still far from the Earth, a means of deflecting the asteroid is to directly alter its momentum by colliding a spacecraft with the asteroid.
A  The European Union's NEOShield-2 Mission is also primarily studying the Kinetic Impactor mitigation method. The principle of the kinetic impactor mitigation method is that the NEO or Asteroid is deflected following an impact from an impactor spacecraft. The principle of momentum transfer is used, as the impactor crashes into the NEO at a very high velocity of or more. The momentum of the impactor is transferred to the NEO, causing a change in velocity and therefore making it deviate from its course slightly.
As of mid-2021, the modified AIDA (mission), AIDA mission has been approved. The NASA Double Asteroid Redirection Test (''DART'') kinetic impactor spacecraft was launched in November 2021. The goal was to impact
The European Union's NEOShield-2 Mission is also primarily studying the Kinetic Impactor mitigation method. The principle of the kinetic impactor mitigation method is that the NEO or Asteroid is deflected following an impact from an impactor spacecraft. The principle of momentum transfer is used, as the impactor crashes into the NEO at a very high velocity of or more. The momentum of the impactor is transferred to the NEO, causing a change in velocity and therefore making it deviate from its course slightly.
As of mid-2021, the modified AIDA (mission), AIDA mission has been approved. The NASA Double Asteroid Redirection Test (''DART'') kinetic impactor spacecraft was launched in November 2021. The goal was to impact

 * In their 1964 book, ''Islands in Space'', Dandridge M. Cole and Donald W. Cox noted the dangers of planetoid impacts, both those occurring naturally and those that might be brought about with hostile intent. They argued for cataloging the minor planets and developing the technologies to land on, deflect, or even capture planetoids.
* In 1967, students in the Aeronautics and Astronautics department at MIT did a design study, "Project Icarus", of a mission to prevent a hypothetical impact on Earth by asteroid 1566 Icarus. The design project was later published in a book by the MIT Press and received considerable publicity, for the first time bringing asteroid impact into the public eye.
* In the 1980s NASA studied evidence of past strikes on planet Earth, and the risk of this happening at the current level of civilization. This led to a program that maps objects in the Solar System that both cross Earth's orbit and are large enough to cause serious damage if they hit.
* In the 1990s, US Congress held hearings to consider the risks and what needed to be done about them. This led to a US$3 million annual budget for programs like
* In their 1964 book, ''Islands in Space'', Dandridge M. Cole and Donald W. Cox noted the dangers of planetoid impacts, both those occurring naturally and those that might be brought about with hostile intent. They argued for cataloging the minor planets and developing the technologies to land on, deflect, or even capture planetoids.
* In 1967, students in the Aeronautics and Astronautics department at MIT did a design study, "Project Icarus", of a mission to prevent a hypothetical impact on Earth by asteroid 1566 Icarus. The design project was later published in a book by the MIT Press and received considerable publicity, for the first time bringing asteroid impact into the public eye.
* In the 1980s NASA studied evidence of past strikes on planet Earth, and the risk of this happening at the current level of civilization. This led to a program that maps objects in the Solar System that both cross Earth's orbit and are large enough to cause serious damage if they hit.
* In the 1990s, US Congress held hearings to consider the risks and what needed to be done about them. This led to a US$3 million annual budget for programs like
boulder.swri.edu
* Donald W. Cox, and James H. Chestek. 1996. ''Doomsday Asteroid: Can We Survive?'' New York: Prometheus Books. . (Note that despite its sensationalist title, this is a good treatment of the subject and includes a nice discussion of the collateral space development possibilities.) * Izzo, D., Bourdoux, A., Walker, R. and Ongaro, F.; "Optimal Trajectories for the Impulsive Deflection of NEOs"; Paper IAC-05-C1.5.06, 56th International Astronautical Congress, Fukuoka, Japan, (October 2005). Later published in Acta Astronautica, Vol. 59, No. 1-5, pp. 294–300, April 2006, available i
esa.int – The first scientific paper proving that Apophis can be deflected by a small sized kinetic impactor.
* David Morrison
''Skeptical Inquirer'' 1997.
David Morrison, Alan W Harris, Geoff Summer, Clark R. Chapman, & Andrea Carusi ''Dealing with Impact Hazard'', 2002 technical summary
* Kunio M. Sayanagi
"How to Deflect an Asteroid"
''Ars Technica'' (April 2008). * Russell L. Schweickart, Edward T. Lu, Piet Hut and Clark R. Chapman; "The Asteroid Tugboat"; ''Scientific American'' (November 2003). Vol. 289, No. 5, pp. 54–61. .
Planetary Defense: Social, Economic, and Political Implications
', United States Air Force, Air Force 2025 Final Report webpage, December 11, 1996. * Belton, M.J.S.
Mitigation of Hazardous Comets and Asteroids
', Cambridge University Press, 2004, * Bottke, William F.
Asteroids III
' (Space Science Series), University of Arizona space science series, University of Arizona Press, 2002, * Burrows, William E
''The Asteroid Threat: Defending Our Planet from Deadly Near-Earth Objects''
* Lewis, John S.
Comet and Asteroid Impact Hazards on a Populated Earth: Computer Modeling
' (Volume 1 of Comet and Asteroid Impact Hazards on a Populated Earth: Computer Modeling), Academic Press, 2000, * Marboe, Irmgard : ''Legal Aspects of Planetary Defence.'' Brill, Leiden 2021, ISBN 978-90-04-46759-0. * Schmidt, Nikola et al.: ''Planetary Defense: Global Collaboration for Defending Earth from Asteroids and Comets.'' Springer, Cham 2019, . * Verschuur, Gerrit L. (1997
''Impact!: The Threat of Comets and Asteroids''
Oxford University Press,
"Deflecting Asteroids"
(with solar sails) by Gregory L. Matloff, ''IEEE Spectrum'', April 2012
Near Earth Objects Directory
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20100325002654/http://star.arm.ac.uk/impact-hazard/ Armagh University: Near Earth Object Impact Hazard ]
Threats from Space: A Review of U.S. Government Efforts to Track and Mitigate Asteroids and Meteors (Part I and Part II): Hearing before the Committee on Science, Space, and Technology, House of Representatives, One Hundred Thirteenth Congress, First Session, Tuesday, March 19, 2013 and Wednesday, April 10, 2013
{{DEFAULTSORT:Asteroid Impact Avoidance Planetary defense, * Asteroids Earth Future problems Impact events Prevention Space weapons
 Asteroid impact avoidance comprises the methods by which
Asteroid impact avoidance comprises the methods by which near-Earth object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). ...
s (NEO) on a potential collision course with Earth could be diverted away, preventing destructive impact events. An impact by a sufficiently large asteroid or other NEOs would cause, depending on its impact location, massive tsunamis
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater expl ...
or multiple firestorm
A firestorm is a conflagration which attains such intensity that it creates and sustains its own wind system. It is most commonly a natural phenomenon, created during some of the largest bushfires and wildfires. Although the term has been used ...
s, and an impact winter
An impact winter is a hypothesized period of prolonged cold weather due to the impact of a large asteroid or comet on the Earth's surface. If an asteroid were to strike land or a shallow body of water, it would eject an enormous amount of dust, ...
caused by the sunlight-blocking effect of large quantities of pulverized rock dust and other debris placed into the stratosphere. A collision 66 million years ago between the Earth and an object approximately wide is thought to have produced the Chicxulub crater
The Chicxulub crater () is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large a ...
and triggered the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
that is understood by the scientific community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many " sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional activities are als ...
to have caused the extinction of all non-avian dinosaurs.
While the chances of a major collision are low in the near term, it is a near-certainty
Certainty (also known as epistemic certainty or objective certainty) is the epistemic property of beliefs which a person has no rational grounds for doubting. One standard way of defining epistemic certainty is that a belief is certain if and o ...
that one will happen eventually unless defensive measures are taken. Astronomical events—such as the Shoemaker-Levy 9 impacts on Jupiter and the 2013 Chelyabinsk meteor, along with the growing number of near-Earth objects discovered and catalogued on the Sentry Risk Table
Sentry is a highly automated impact prediction system operated by the JPL Center for NEO Studies (CNEOS) since 2002. It continually monitors the most up-to-date asteroid catalog for possibilities of future impact with Earth over the next 100+ y ...
—have drawn renewed attention to such threats. The popularity of the 2021 movie ''Don't Look Up
''Don't Look Up'' is a 2021 American apocalyptic political satire black comedy film written, co-produced, and directed by Adam McKay from a story he co-wrote with David Sirota. It stars Leonardo DiCaprio, Jennifer Lawrence, Rob Morgan, ...
'' helped to raise awareness of the possibility of avoiding NEOs.
In 2016, a NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
scientist warned that the Earth is unprepared for such an event. In April 2018, the B612 Foundation
The B612 Foundation is a private nonprofit foundation headquartered in Mill Valley, California, United States, dedicated to planetary science and planetary defense against asteroids and other near-Earth object (NEO) impacts. It is led mainl ...
reported "It's 100 percent certain we'll be hit by a devastating asteroid, but we're not 100 percent sure when." Also in 2018, physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
Stephen Hawking, in his final book, ''Brief Answers to the Big Questions
''Brief Answers to the Big Questions'' is a popular science book written by physicist Stephen Hawking, and published by Hodder & Stoughton (hardcover) and Bantam Books (paperback) on 16 October 2018. The book examines some of the universe gre ...
'', considered an asteroid collision to be the biggest threat to the planet. Several ways of avoiding an asteroid impact have been described. Nonetheless, in March 2019, scientists reported that asteroids may be much more difficult to destroy than thought earlier. In addition, an asteroid may reassemble itself due to gravity after being disrupted. In May 2021, NASA astronomers reported that 5 to 10 years of preparation may be needed to avoid a virtual impactor based on a simulated exercise conducted by the 2021 Planetary Defense Conference.
In 2022, NASA spacecraft DART impacted Dimorphos
(65803) Didymos I Dimorphos (provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a minor-planet moon of the near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a binary system. It has a diameter of and has been characterised as a low-density rubb ...
, reducing the minor-planet moon's orbital period by 32 minutes. This mission constitues the first successful attempt at asteroid deflection. Deflection efforts

 According to expert testimony in the
According to expert testimony in the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
in 2013, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
would require at least five years of preparation before a mission to intercept an asteroid could be launched. In June 2018, the US National Science and Technology Council
The National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) is a council in the Executive Branch of the United States. It is designed to coordinate science and technology policy across the branches of federal government.
History
The National Science and ...
warned that the United States was unprepared for an asteroid impact event, and developed and released the "National Near-Earth Object Preparedness Strategy Action Plan" to better prepare.
Most deflection efforts for a large object require from a year to decades of warning, allowing time to prepare and carry out a collision avoidance project, as no known planetary defense hardware has yet been developed. It has been estimated that a velocity change of just (where t is the number of years until potential impact) is needed to successfully deflect a body on a direct collision trajectory. In addition, under certain circumstances, much smaller velocity changes are needed.S.-Y. Park and I. M. Ross, "Two-Body Optimization for Deflecting Earth-Crossing Asteroids", ''Journal of Guidance, Control and Dynamics'', Vol. 22, No.3, 1999, pp.415–420. For example, it was estimated there was a high chance of 99942 Apophis
99942 Apophis is a near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous asteroid with a diameter of that caused a brief period of concern in December 2004 when initial observations indicated a probability up to 2.7% that it would hit Earth on April&nb ...
swinging by Earth in 2029 with a 10−4 probability of returning on an impact trajectory in 2035 or 2036. It was then determined that a deflection from this potential return trajectory, several years before the swing-by, could be achieved with a velocity change on the order of 10−6 m·s−1.
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), the world’s first full-scale mission to test technology for defending Earth against potential asteroid or comet hazards, launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
An impact by a asteroid on the Earth has historically caused an extinction-level event due to catastrophic damage to the biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
. There is also the threat from comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s entering the inner Solar System. The impact speed of a long-period comet would likely be several times greater than that of a near-Earth asteroid, making its impact much more destructive; in addition, the warning time is unlikely to be more than a few months. Impacts from objects as small as in diameter, which are far more common, are historically extremely destructive regionally (see Barringer crater).
Finding out the material composition of the object is also helpful before deciding which strategy is appropriate. Missions like the 2005 '' Deep Impact'' probe and the Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Ro ...
spacecraft, have provided valuable information on what to expect. In October 2022, a method of mapping the insides of a potentially problematic asteroid in order to determine the best area for impact was proposed.
History of US government mandates
Efforts inasteroid impact prediction
Asteroid impact prediction is the prediction of the dates and times of asteroids impacting Earth, along with the locations and severities of the impacts.
The process of impact prediction follows three major steps:
# Discovery of an asteroid and ...
have concentrated on the survey method. The 1992 NASA-sponsored Near-Earth-Object Interception Workshop hosted by Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
evaluated issues involved in intercepting celestial objects that could hit Earth. In a 1992 report to NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
,Morrison, D., 25 January 1992''The Spaceguard Survey: Report of the NASA International Near-Earth-Object Detection Workshop''
,
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
, Washington, D.C. a coordinated Spaceguard
The term Spaceguard loosely refers to a number of efforts to discover, catalogue, and study near-Earth objects (NEO), especially those that may impact Earth ( potentially hazardous objects).
Asteroids are discovered by telescopes which repeate ...
Survey was recommended to discover, verify and provide follow-up observations for Earth-crossing asteroids. This survey was expected to discover 90% of these objects larger than one kilometer within 25 years. Three years later, another NASA report recommended search surveys that would discover 60–70% of short-period, near-Earth objects larger than one kilometer within ten years and obtain 90% completeness within five more years.
In 1998, NASA formally embraced the goal of finding and cataloging, by 2008, 90% of all near-Earth objects (NEOs) with diameters of 1 km or larger that could represent a collision risk to Earth. The 1 km diameter metric was chosen after considerable study indicated that an impact of an object smaller than 1 km could cause significant local or regional damage but is unlikely to cause a worldwide catastrophe. The impact of an object much larger than 1 km diameter could well result in worldwide damage up to, and potentially including, extinction of the human species. The NASA commitment has resulted in the funding of a number of NEO search efforts, which made considerable progress toward the 90% goal by 2008. However the 2009 discovery of several NEOs approximately 2 to 3 kilometers in diameter (e.g. , , , and ) demonstrated there were still large objects to be detected.
United States Representative George E. Brown Jr. (D-CA) was quoted as voicing his support for planetary defense projects in ''Air & Space Power Chronicles'', saying "If some day in the future we discover well in advance that an asteroid that is big enough to cause a mass extinction is going to hit the Earth, and then we alter the course of that asteroid so that it does not hit us, it will be one of the most important accomplishments in all of human history."
Because of Congressman Brown's long-standing commitment to planetary defense, a U.S. House of Representatives' bill, H.R. 1022, was named in his honor: The George E. Brown, Jr. Near-Earth Object Survey Act. This bill "to provide for a Near-Earth Object Survey program to detect, track, catalogue, and characterize certain near-Earth asteroids and comets" was introduced in March 2005 by Rep. Dana Rohrabacher
Dana Tyrone Rohrabacher (; born June 21, 1947) is a former American politician who served in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1989 to 2019. A Republican, he represented for the last three terms of his House tenure.
Rohrabacher ran for r ...
(R-CA). It was eventually rolled into S.1281, the NASA Authorization Act of 2005
The NASA Authorization Act of 2005 is an act of the United States Congress that requires NASA to carry out a balanced set of programs in human spaceflight, in aeronautics research and development and in scientific research. It was signed by the t ...
, passed by Congress on December 22, 2005, subsequently signed by the President, and stating in part:
The result of this directive was a report presented to Congress in early March 2007. This was an Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) study led by NASA's Program Analysis and Evaluation (PA&E) office with support from outside consultants, the Aerospace Corporation, NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC), and SAIC (amongst others).
See also Improving impact prediction.
Ongoing projects

 The Minor Planet Center in
The Minor Planet Center in Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston ...
has been cataloging the orbits of asteroids and comets since 1947. It has recently been joined by surveys that specialize in locating the near-Earth object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). ...
s (NEO), many (as of early 2007) funded by NASA's Near Earth Object program office as part of their Spaceguard program. One of the best-known is LINEAR
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship ('' function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear ...
that began in 1996. By 2004 LINEAR was discovering tens of thousands of objects each year and accounting for 65% of all new asteroid detections. LINEAR uses two one-meter telescopes and one half-meter telescope based in New Mexico.
The Catalina Sky Survey
Catalina Sky Survey (CSS; obs. code: 703) is an astronomical survey to discover comets and asteroids. It is conducted at the Steward Observatory's Catalina Station, located near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States.
CSS focuses on the search ...
(CSS) is conducted at the Steward Observatory
Steward Observatory is the research arm of the Department of Astronomy at the University of Arizona (UArizona). Its offices are located on the UArizona campus in Tucson, Arizona (US). Established in 1916, the first telescope and building were f ...
's Catalina Station
Catalina Station (CS), also known as Steward Observatory Catalina Station, is an astronomical observing facility located on Mount Bigelow in the Santa Catalina Mountains approximately northeast of Tucson, Arizona. The site in the Coronado Nati ...
, located near Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
, in the United States. It uses two telescopes, a 1.5-meter (60-inch) f/2 telescope on the peak of Mount Lemmon
Mount Lemmon, with a summit elevation of , is the highest point in the Santa Catalina Mountains. It is located in the Coronado National Forest north of Tucson, Arizona, United States. Mount Lemmon was named for botanist Sara Plummer Lemmon, who ...
, and a 68-cm (27-inch) f/1.7 Schmidt
Schmidt may refer to:
* Schmidt (surname), including list of people with the surname
* Schmidt (singer) (born 1990), German pop and jazz singer
* Schmidt (lunar crater), a small lunar impact crater
* Schmidt (Martian crater), a List of craters on ...
telescope near Mount Bigelow (both in the Tucson, Arizona area). In 2005, CSS became the most prolific NEO survey surpassing Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research
The Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) project is a collaboration of the United States Air Force, NASA, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory for the systematic detection and tracking of near-Earth objects ...
(LINEAR) in total number of NEOs and potentially hazardous asteroids discovered each year since. CSS discovered 310 NEOs in 2005, 396 in 2006, 466 in 2007, and in 2008 564 NEOs were found.
Spacewatch
The Spacewatch Project is an astronomical survey that specializes in the study of minor planets, including various types of asteroids and comets at University of Arizona telescopes on Kitt Peak near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. The Spa ...
, which uses a 90 centimeter telescope sited at the Kitt Peak Observatory
The Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) is a United States astronomical observatory located on Kitt Peak of the Quinlan Mountains in the Arizona-Sonoran Desert on the Tohono Oʼodham Nation, west-southwest of Tucson, Arizona. With more than ...
in Arizona, updated with automatic pointing, imaging, and analysis equipment to search the skies for intruders, was set up in 1980 by Tom Gehrels
Anton M.J. "Tom" Gehrels (February 21, 1925 – July 11, 2011) was a Dutch–American astronomer, Professor of Planetary Sciences, and Astronomer at the University of Arizona, Tucson.
Biography
Youth and education
Gehrels was born at Haa ...
and Robert S. McMillan of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory of the University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a public land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first university in the Arizona Territory.
T ...
in Tucson, and is now being operated by McMillan. The Spacewatch project has acquired a 1.8 meter telescope, also at Kitt Peak, to hunt for NEOs, and has provided the old 90-centimeter telescope with an improved electronic imaging system with much greater resolution, improving its search capability.
Other near-Earth object tracking programs include Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking
Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) was a program run by NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, surveying the sky for near-Earth objects. NEAT was conducted from December 1995 until April 2007, at GEODSS on Hawaii (Haleakala-NEAT; 566), as we ...
(NEAT), Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search
Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search (LONEOS) was a project designed to discover asteroids and comets that orbit near the Earth. The project, funded by NASA, was directed by astronomer Ted Bowell of Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizo ...
(LONEOS), Campo Imperatore Near-Earth Object Survey
The CINEOS program (Campo Imperatore Near-Earth Object Survey), started in 2001, is dedicated to the discovery and follow-up of near-Earth objects (NEOs), namely asteroids and comets which periodically approach or intersect the Earth's orbit. In ...
(CINEOS), Japanese Spaceguard Association
The is a not-for-profit organization based in Tokyo, Japan. Its formal status under the Japanese law is .
Missions
The aims of the Japan Spaceguard Association (JSGA) echoes that of The Spaceguard Foundation and other spaceguard movements: to ...
, and Asiago-DLR Asteroid Survey
The Asiago-DLR Asteroid Survey (ADAS; obs. code: 209) was an astronomical survey conducted in the early 2000s to search for comets and asteroids, with special emphasis on near-Earth objects. The Minor Planet Center directly credits ADA ...
. Pan-STARRS
The Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System (Pan-STARRS1; obs. code: F51 and Pan-STARRS2 obs. code: F52) located at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, US, consists of astronomical cameras, telescopes and a computing facility that is ...
completed telescope construction in 2010, and it is now actively observing.
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) is a robotic astronomical survey and early warning system optimized for detecting smaller near-Earth objects a few weeks to days before they impact Earth.
Funded by NASA, and developed an ...
, now in operation, conducts frequent scans of the sky with a view to later-stage detection on the collision stretch of the asteroid orbit. Those would be much too late for deflection, but still in time for evacuation and preparation of the affected Earth region.
Another project, supported by the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, is NEOShield, which analyses realistic options for preventing the collision of a NEO with Earth. Their aim is to provide test mission designs for feasible NEO mitigation concepts. The project particularly emphasises on two aspects.
# The first one is the focus on technological development on essential techniques and instruments needed for guidance, navigation and control (GNC) in close vicinity of asteroids and comets. This will, for example, allow hitting such bodies with a high-velocity kinetic impactor spacecraft and observing them before, during and after a mitigation attempt, e.g., for orbit determination and monitoring.
# The second one focuses on refining Near Earth Object (NEO) characterisation. Moreover, NEOShield-2 will carry out astronomical observations of NEOs, to improve the understanding of their physical properties, concentrating on the smaller sizes of most concern for mitigation purposes, and to identify further objects suitable for missions for physical characterisation and NEO deflection demonstration.
"Spaceguard
The term Spaceguard loosely refers to a number of efforts to discover, catalogue, and study near-Earth objects (NEO), especially those that may impact Earth ( potentially hazardous objects).
Asteroids are discovered by telescopes which repeate ...
" is the name for these loosely affiliated programs, some of which receive NASA funding to meet a U.S. Congressional requirement to detect 90% of near-Earth asteroids over 1 km diameter by 2008. A 2003 NASA study of a follow-on program suggests spending US$250–450 million to detect 90% of all near-Earth asteroids 140 meters and larger by 2028.
NEODyS
NEODyS (Near Earth Objects Dynamic Site) is an Italian service that provides information on near-Earth objects with a Web-based interface. It is based on a continually and (almost) automatically maintained database of near earth asteroid orbits. T ...
is an online database of known NEOs.
Sentinel mission
TheB612 Foundation
The B612 Foundation is a private nonprofit foundation headquartered in Mill Valley, California, United States, dedicated to planetary science and planetary defense against asteroids and other near-Earth object (NEO) impacts. It is led mainl ...
is a private nonprofit foundation
Foundation may refer to:
* Foundation (nonprofit), a type of charitable organization
** Foundation (United States law), a type of charitable organization in the U.S.
** Private foundation, a charitable organization that, while serving a good cause ...
with headquarters in the United States, dedicated to protecting the Earth from asteroid strikes. It is led mainly by scientists, former astronauts and engineers from the Institute for Advanced Study
The Institute for Advanced Study (IAS), located in Princeton, New Jersey, in the United States, is an independent center for theoretical research and intellectual inquiry. It has served as the academic home of internationally preeminent schola ...
, Southwest Research Institute, Stanford University, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
and the space industry
Space industry refers to economic activities related to manufacturing components that go into Earth's orbit or beyond, delivering them to those regions, and related services. Owing to the prominence of the satellite-related activities, some sour ...
.
As a non-governmental organization it has conducted two lines of related research to help detect NEOs that could one day strike the Earth, and find the technological means to divert their path to avoid such collisions. The foundation's goal had been to design and build a privately financed asteroid-finding space telescope
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launch ...
, Sentinel
Sentinel may refer to:
Places Mountains
* Mount Sentinel, a mountain next to the University of Montana in Missoula, Montana
* Sentinel Buttress, a volcanic crag on James Ross Island, Antarctica
* Sentinel Dome, a naturally occurring grani ...
, which was to be launched in 2017–2018. However the project was cancelled in 2015. Had the Sentinel's infrared telescope been parked in an orbit similar to that of Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, it would have helped identify threatening NEOs by cataloging 90% of those with diameters larger than , as well as surveying smaller Solar System objects.Powell, Corey S"Developing Early Warning Systems for Killer Asteroids"
, ''
Discover
Discover may refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''Discover'' (album), a Cactus Jack album
* ''Discover'' (magazine), an American science magazine
Businesses and brands
* DISCover, the ''Digital Interactive Systems Corporation''
* D ...
'', August 14, 2013, pp. 60–61 (subscription required).
Data gathered by Sentinel would have helped identify asteroids and other NEOs that pose a risk of collision with Earth, by being forwarded to scientific data-sharing networks, including NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
and academic institutions such as the Minor Planet Center.Broad, William JVindication for Entrepreneurs Watching Sky: Yes, It Can Fall
, ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' website, February 16, 2013 and in print on February 17, 2013, p. A1 of the New York edition. Retrieved June 27, 2014. The foundation also proposes asteroid deflection of potentially dangerous NEOs by the use of gravity tractor
A gravity tractor is a theoretical spacecraft that would deflect another object in space, typically a potentially hazardous asteroid that might impact Earth, without physically contacting it, using only its gravitational field to transmit the requ ...
s to divert their trajectories away from Earth,Powell, Corey SHow to Deflect a Killer Asteroid: Researchers Come Up With Contingency Plans That Could Help Our Planet Dodge A Cosmic Bullet
, ''
Discover
Discover may refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''Discover'' (album), a Cactus Jack album
* ''Discover'' (magazine), an American science magazine
Businesses and brands
* DISCover, the ''Digital Interactive Systems Corporation''
* D ...
'' website, September 18, 2013 (subscription required), and in print as "How to Dodge a Cosmic Bullet", October 2013. Retrieved July 15, 2014. a concept co-invented by the organization's CEO, physicist and former NASA astronaut Ed Lu
Edward Tsang "Ed" Lu (; born July 1, 1963) is an American physicist and former NASA astronaut. He flew on two Space Shuttle flights, and made an extended stay aboard the International Space Station.
In 2007, Lu retired from NASA to become the pr ...
.
Prospective projects
Orbit@home
orbit@home was a BOINC-based volunteer computing project of the Planetary Science Institute. It uses the "Orbit Reconstruction, Simulation and Analysis" framework to optimize the search strategies that are used to find near-Earth objects.
On M ...
intends to provide distributed computing resources to optimize search strategy. On February 16, 2013, the project was halted due to lack of grant funding. However, on July 23, 2013, the orbit@home project was selected for funding by NASA's Near Earth Object Observation program and was to resume operations sometime in early 2014. As of July 13, 2018, the project is offline according to its website.
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, previously referred to as the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST), is an astronomical observatory currently under construction in Chile. Its main task will be carrying out a synoptic astronomical survey, the Le ...
, currently under construction, is expected to perform a comprehensive, high-resolution survey starting in the early 2020s.
Detection from space
On November 8, 2007, theHouse Committee on Science and Technology
The Committee on Science, Space, and Technology is a committee of the United States House of Representatives. It has jurisdiction over non-defense federal scientific research and development. More specifically, the committee has complete jurisdic ...
's Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics held a hearing to examine the status of NASA's Near-Earth Object survey program. The prospect of using the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 201 ...
was proposed by NASA officials.
WISE surveyed the sky in the infrared band at a very high sensitivity. Asteroids that absorb solar radiation can be observed through the infrared band. It was used to detect NEOs, in addition to performing its science goals. It is projected that WISE could detect 400 NEOs (roughly two percent of the estimated NEO population of interest) within the one-year mission.
NEOSSat, the Near Earth Object Surveillance Satellite, is a microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. ...
launched in February 2013 by the Canadian Space Agency
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA; french: Agence spatiale canadienne, ASC) is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the ''Canadian Space Agency Act''.
The president is Lisa Campbell, who took the position on September 3, 2020 ...
(CSA) that will hunt for NEOs in space. Furthermore Near-Earth Object WISE (NEOWISE), an extension of the WISE mission, started in September 2013 (in its second mission extension) to hunt asteroids and comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s close to the orbit of Earth.
''Deep Impact''
Research published in the March 26, 2009 issue of the journal ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
'', describes how scientists were able to identify an asteroid in space before it entered Earth's atmosphere, enabling computers to determine its area of origin in the Solar System as well as predict the arrival time and location on Earth of its shattered surviving parts. The four-meter-diameter asteroid, called 2008 TC3, was initially sighted by the automated Catalina Sky Survey
Catalina Sky Survey (CSS; obs. code: 703) is an astronomical survey to discover comets and asteroids. It is conducted at the Steward Observatory's Catalina Station, located near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States.
CSS focuses on the search ...
telescope, on October 6, 2008. Computations correctly predicted that it would impact 19 hours after discovery and in the Nubian Desert
The Nubian Desert ( ar, صحراء النوبة, ''Şaḩrā’ an Nūbyah'') is in the eastern region of the Sahara Desert, spanning approximately 400,000 km2 of northeastern Sudan and northern Eritrea, between the Nile and the Red Sea. Th ...
of northern Sudan.
A number of potential threats have been identified, such as 99942 Apophis
99942 Apophis is a near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous asteroid with a diameter of that caused a brief period of concern in December 2004 when initial observations indicated a probability up to 2.7% that it would hit Earth on April&nb ...
(previously known by its provisional designation
Provisional designation in astronomy is the naming convention applied to astronomical objects immediately following their discovery. The provisional designation is usually superseded by a permanent designation once a reliable orbit has been calcu ...
), which in 2004 temporarily had an impact probability of about 3% for the year 2029. Additional observations revised this probability down to zero.
''Double Asteroid Redirection Test''
On September 26, 2022 '' DART'' impactedDimorphos
(65803) Didymos I Dimorphos (provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a minor-planet moon of the near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a binary system. It has a diameter of and has been characterised as a low-density rubb ...
, reducing the minor-planet moon's orbital period by 32 minutes. This mission was the first successful attempt at asteroid deflection.
Impact probability calculation pattern
The ellipses in the diagram on the right show the predicted position of an example asteroid at closest Earth approach. At first, with only a few asteroid observations, the error ellipse is very large and includes the Earth. Further observations shrink the error ellipse, but it still includes the Earth. This raises the predicted impact probability, since the Earth now covers a larger fraction of the error region. Finally, yet more observations (often radar observations, or discovery of a previous sighting of the same asteroid on archival images) shrink the ellipse revealing that the Earth is outside the error region, and the impact probability is near zero. For asteroids that are actually on track to hit Earth the predicted probability of impact continues to increase as more observations are made. This similar pattern makes it difficult to differentiate between asteroids that will only come close to Earth and those that will actually hit it. This in turn makes it difficult to decide when to raise an alarm as gaining more certainty takes time, which reduces time available to react to a predicted impact. However, raising the alarm too soon has the danger of causing afalse alarm
A false alarm, also called a nuisance alarm, is the deceptive or erroneous report of an emergency, causing unnecessary panic and/or bringing resources (such as emergency services) to a place where they are not needed. False alarms may occur with ...
and creating a Boy Who Cried Wolf
The Boy Who Cried Wolf is one of Aesop's Fables, numbered 210 in the Perry Index. From it is derived the English idiom "to cry wolf", defined as "to give a false alarm" in e''Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable'' and glossed by the ''Oxford E ...
effect if the asteroid in fact misses Earth.
Collision avoidance strategies
Various collision avoidance techniques have different trade-offs with respect to metrics such as overall performance, cost, failure risks, operations, and technology readiness. There are various methods for changing the course of an asteroid/comet.C. D. Hall and I. M. Ross, "Dynamics and Control Problems in the Deflection of Near-Earth Objects", ''Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, Astrodynamics 1997'', Vol.97, Part I, 1997, pp.613–631. These can be differentiated by various types of attributes such as the type of mitigation (deflection or fragmentation), energy source (kinetic, electromagnetic, gravitational, solar/thermal, or nuclear), and approach strategy (interception, rendezvous, or remote station). Strategies fall into two basic sets: Fragmentation and delay. Fragmentation concentrates on rendering the impactor harmless by fragmenting it and scattering the fragments so that they miss the Earth or are small enough to burn up in the atmosphere. Delay exploits the fact that both the Earth and the impactor are in orbit. An impact occurs when both reach the same point in space at the same time, or more correctly when some point on Earth's surface intersects the impactor's orbit when the impactor arrives. Since the Earth is approximately 12,750 km in diameter and moves at approx. 30 km per second in its orbit, it travels a distance of one planetary diameter in about 425 seconds, or slightly over seven minutes. Delaying, or advancing the impactor's arrival by times of this magnitude can, depending on the exact geometry of the impact, cause it to miss the Earth. Collision avoidance strategies can also be seen as either direct, or indirect and in how rapidly they transfer energy to the object. The direct methods, such as nuclear explosives, or kinetic impactors, rapidly intercept the bolide's path. Direct methods are preferred because they are generally less costly in time and money. Their effects may be immediate, thus saving precious time. These methods would work for short-notice and long-notice threats, and are most effective against solid objects that can be directly pushed, but in the case of kinetic impactors, they are not very effective against large loosely aggregated rubble piles. Indirect methods, such asgravity tractor
A gravity tractor is a theoretical spacecraft that would deflect another object in space, typically a potentially hazardous asteroid that might impact Earth, without physically contacting it, using only its gravitational field to transmit the requ ...
s, attaching rockets or mass drivers, are much slower. They require traveling to the object, changing course up to 180 degrees for space rendezvous
A space rendezvous () is a set of orbital maneuvers during which two spacecraft, one of which is often a space station, arrive at the same orbit and approach to a very close distance (e.g. within visual contact). Rendezvous requires a precise ma ...
, and then taking much more time to change the asteroid's path just enough so it will miss Earth.
Many NEOs are thought to be "flying rubble pile
In astronomy, a rubble pile is a celestial body that is not a monolith, consisting instead of numerous pieces of rock that have coalesced under the influence of gravity. Rubble piles have low density because there are large cavities between the ...
s" only loosely held together by gravity, and a typical spacecraft sized kinetic-impactor deflection attempt might just break up the object or fragment it without sufficiently adjusting its course.Planetary Defense Conference 2007, Washington D.C. Head-On Impact Deflection of NEAs: A Case Study for 99942 Apophis. Bernd Dachwald, Ralph Kahle, Bong Wie, Published in 2007.pg 3If an asteroid breaks into fragments, any fragment larger than 35 meters across would not burn up in the atmosphere and itself could impact Earth. Tracking the thousands of
buckshot
A shotgun shell, shotshell or simply shell is a type of rimmed, cylindrical (straight-walled) cartridges used specifically in shotguns, and is typically loaded with numerous small, pellet-like spherical sub-projectiles called shot, fired throu ...
-like fragments that could result from such an explosion would be a very daunting task, although fragmentation would be preferable to doing nothing and allowing the originally larger rubble body, which is analogous to a shot and wax slug, to impact the Earth.
In Cielo (supercomputer), Cielo simulations conducted in 2011–2012, in which the rate and quantity of energy delivery were sufficiently high and matched to the size of the rubble pile, such as following a tailored nuclear explosion, results indicated that any asteroid fragments, created after the pulse of energy is delivered, would not pose a threat of re-coalescence (physics), coalescing (including for those with the shape of asteroid 25143 Itokawa, Itokawa) but instead would rapidly achieve escape velocity from their parent body (which for Itokawa is about 0.2 m/s) and therefore move out of an earth-impact trajectory.
Nuclear explosive device
 Initiating a nuclear explosive device proximity fuze, above, impact fuze, on, or slightly Robust Nuclear Earth Penetrator, beneath, the surface of a threatening celestial body is a potential deflection option, with the optimal detonation height dependent upon the composition and size of the object. It does not require the entire NEO to be vaporized to mitigate an impact threat. In the case of an inbound threat from a "rubble pile," the proximity fuze, stand off, or detonation height above the surface configuration, has been put forth as a means to prevent the potential fracturing of the rubble pile. The energetic neutrons and soft X-rays released by the detonation, which do not appreciably penetrate matter, are converted into heat upon encountering the object's surface matter, radiation implosion, ablatively vaporizing all Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight exposed surface areas of the object to a shallow depth, turning the surface material it heats up into ejecta, and, analogous to the ejecta from a chemical rocket engine exhaust, changing the velocity, or "nudging", the object off course by the reaction, following Newton's third law, with ejecta going one way and the object being propelled in the other.
Initiating a nuclear explosive device proximity fuze, above, impact fuze, on, or slightly Robust Nuclear Earth Penetrator, beneath, the surface of a threatening celestial body is a potential deflection option, with the optimal detonation height dependent upon the composition and size of the object. It does not require the entire NEO to be vaporized to mitigate an impact threat. In the case of an inbound threat from a "rubble pile," the proximity fuze, stand off, or detonation height above the surface configuration, has been put forth as a means to prevent the potential fracturing of the rubble pile. The energetic neutrons and soft X-rays released by the detonation, which do not appreciably penetrate matter, are converted into heat upon encountering the object's surface matter, radiation implosion, ablatively vaporizing all Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight exposed surface areas of the object to a shallow depth, turning the surface material it heats up into ejecta, and, analogous to the ejecta from a chemical rocket engine exhaust, changing the velocity, or "nudging", the object off course by the reaction, following Newton's third law, with ejecta going one way and the object being propelled in the other.Depending on the energy of the explosive device, the resulting reaction engine, rocket exhaust effect, created by the high velocity of the asteroid's vaporized mass ejecta, coupled with the object's small reduction in mass, would produce enough of a change in the object's orbit to make it miss the Earth. A Hypervelocity Asteroid Mitigation Mission for Emergency Response (HAMMER) has been proposed.
Stand-off approach
If the object is very large but is still a loosely-held-together rubble pile, a solution is to detonate one or a series of nuclear explosive devices alongside the asteroid, at a or greater stand-off height above its surface, so as not to fracture the potentially loosely-held-together object. Providing that this stand-off strategy was done far enough in advance, the force from a sufficient number of nuclear blasts would alter the object's trajectory enough to avoid an impact, according to computer simulations and experimental evidence from meteorites exposed to the thermal X-ray pulses of the Z Pulsed Power Facility, Z-machine. In 1967, graduate students under Professor Paul Sandorff at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology were tasked with designing a method to prevent a hypothetical 18-month distant impact on Earth by the asteroid 1566 Icarus, an object that makes regular close approaches to Earth, sometimes as close as 16 lunar distance (astronomy), lunar distances. To achieve the task within the timeframe and with limited material knowledge of the asteroid's composition, a variable stand-off system was conceived. This would have used a number of modified Saturn V rockets sent on interception courses and the creation of a handful of nuclear explosive devices in the 100-megaton energy range—coincidentally, the same as the maximum yield of the Soviets' Tsar Bomba#Test, ''Tsar Bomba'' would have been if a uranium tamper had been used—as each rocket vehicle's payload."Systems Engineering: Avoiding an Asteroid", ''Time (magazine), Time'', June 16, 1967.Day, Dwayne A.
"Giant bombs on giant rockets: Project Icarus"
, ''The Space Review'', Monday, July 5, 2004 The design study was later published as 1566 Icarus#Project Icarus, Project IcarusKleiman Louis A.
''Project Icarus: an MIT Student Project in Systems Engineering''
, Cambridge, Massachusetts : MIT Press, 1968 which served as the inspiration for the 1979 film ''Meteor (film), Meteor''."MIT Course precept for movie"
, ''The Tech'', MIT, October 30, 1979 A
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
analysis of deflection alternatives, conducted in 2007, stated:
In the same year, NASA released a study where the asteroid 99942 Apophis, Apophis (with a diameter of around ) was assumed to have a much lower rubble pile density () and therefore lower mass than it is now known to have, and in the study, it is assumed to be on an impact trajectory with Earth for the year 2029. Under these hypothetical conditions, the report determines that a "Cradle spacecraft" would be sufficient to deflect it from Earth impact. This conceptual spacecraft contains six B83 nuclear bomb, B83 physics packages, each set for their maximum 1.2-megatonne yield, bundled together and lofted by an Ares V vehicle sometime in the 2020s, with each B83 being proximity fuze, fuzed to detonate over the asteroid's surface at a height of ("1/3 of the objects diameter" as its stand-off), one after the other, with hour-long intervals between each detonation. The results of this study indicated that a single employment of this option "can deflect NEOs of [ diameter] two years before impact, and larger NEOs with at least five years warning".Near Earth Object (NEO) Mitigation Options Using Exploration TechnologiesThese effectiveness figures are considered to be "conservative" by its authors, and only the thermal X-ray output of the B83 devices was considered, while neutron heating was neglected for ease of calculation purposes.
Surface and subsurface use
 In 2011, the director of the Asteroid Deflection Research Center at Iowa State University, Dr. Bong Wie (who had published kinetic impactor deflection studies previously), began to study strategies that could deal with objects when the time to Earth impact was less than one year. He concluded that to provide the required energy, a nuclear explosion or other event that could deliver the same power, are the only methods that can work against a very large asteroid within these time constraints.
This work resulted in the creation of a conceptual Hypervelocity Asteroid Intercept Vehicle (HAIV), which combines a Deep Impact (spacecraft), kinetic impactor to create an initial Impact crater, crater for a follow-up subsurface nuclear detonation within that initial crater, which would generate a high degree of efficiency in the conversion of the nuclear energy that is released in the detonation into propulsion energy to the asteroid.
A similar proposal would use a surface-detonating nuclear device in place of the kinetic impactor to create the initial crater, then using the crater as a rocket nozzle to channel succeeding nuclear detonations.
At the 2014 NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) conference, Wie and his colleagues stated that "we have the solution, using our baseline concept, to be able to mitigate the asteroid-impact threat, with any range of warning." For example, according to their computer models, with a warning time of 30 days, a asteroid would be neutralized by using a single HAIV, with less than 0.1% of the destroyed object's mass potentially striking Earth, which by comparison would be more than acceptable.
As of 2015, Wie has collaborated with the Danish Emergency Asteroid Defence Project (EADP), which ultimately intends to crowdsource sufficient funds to design, build, and store a non-nuclear HAIV spacecraft as planetary insurance. For threatening asteroids too large and/or too close to Earth impact to effectively be deflected by the non-nuclear HAIV approach, nuclear explosive devices (with 5% of the explosive yield than those used for the stand-off strategy) are intended to be swapped in, under international oversight, when conditions arise that necessitate it.
In 2011, the director of the Asteroid Deflection Research Center at Iowa State University, Dr. Bong Wie (who had published kinetic impactor deflection studies previously), began to study strategies that could deal with objects when the time to Earth impact was less than one year. He concluded that to provide the required energy, a nuclear explosion or other event that could deliver the same power, are the only methods that can work against a very large asteroid within these time constraints.
This work resulted in the creation of a conceptual Hypervelocity Asteroid Intercept Vehicle (HAIV), which combines a Deep Impact (spacecraft), kinetic impactor to create an initial Impact crater, crater for a follow-up subsurface nuclear detonation within that initial crater, which would generate a high degree of efficiency in the conversion of the nuclear energy that is released in the detonation into propulsion energy to the asteroid.
A similar proposal would use a surface-detonating nuclear device in place of the kinetic impactor to create the initial crater, then using the crater as a rocket nozzle to channel succeeding nuclear detonations.
At the 2014 NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) conference, Wie and his colleagues stated that "we have the solution, using our baseline concept, to be able to mitigate the asteroid-impact threat, with any range of warning." For example, according to their computer models, with a warning time of 30 days, a asteroid would be neutralized by using a single HAIV, with less than 0.1% of the destroyed object's mass potentially striking Earth, which by comparison would be more than acceptable.
As of 2015, Wie has collaborated with the Danish Emergency Asteroid Defence Project (EADP), which ultimately intends to crowdsource sufficient funds to design, build, and store a non-nuclear HAIV spacecraft as planetary insurance. For threatening asteroids too large and/or too close to Earth impact to effectively be deflected by the non-nuclear HAIV approach, nuclear explosive devices (with 5% of the explosive yield than those used for the stand-off strategy) are intended to be swapped in, under international oversight, when conditions arise that necessitate it.
Comet deflection possibility
 Following the 1994 Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet impacts with Jupiter, Edward Teller proposed, to a collective of U.S. and Russian ex-Cold War weapons designers in a 1995 planetary defense workshop meeting at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), that they collaborate to design a Nuclear weapon design#Arbitrarily large multi-staged devices, one-gigaton nuclear explosive device, which would be equivalent to the kinetic energy of a asteroid.Planetary defense workshop LLNL 1995
Following the 1994 Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet impacts with Jupiter, Edward Teller proposed, to a collective of U.S. and Russian ex-Cold War weapons designers in a 1995 planetary defense workshop meeting at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), that they collaborate to design a Nuclear weapon design#Arbitrarily large multi-staged devices, one-gigaton nuclear explosive device, which would be equivalent to the kinetic energy of a asteroid.Planetary defense workshop LLNL 1995/ref>A new use for nuclear weapons: hunting rogue asteroids A persistent campaign by weapons designers to develop a nuclear defense against extraterrestrial rocks slowly wins government support 2013
The theoretical one-gigaton device would weigh about 25–30 tons, light enough to be lifted on the Energia (rocket), Energia rocket. It could be used to instantaneously vaporize a asteroid, divert the paths of Global catastrophic risk, ELE-class asteroids (greater than in diameter) within short notice of a few months. With one year of notice, and at an interception location no closer than Jupiter, it could also deal with the even rarer List of periodic comets, short period comets that can come out of the Kuiper belt and transit past Earth orbit within two years. For comets of this class, with a maximum estimated diameter of , 2060 Chiron, Chiron served as the hypothetical threat. In 2013, the related National Laboratories of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, US and Rosatom, Russia signed a deal that includes an intent to cooperate on defense from asteroids.
Present capability
An April 2014 GAO report notes that the National Nuclear Security Administration, NNSA is retaining canned subassemblies (CSAs—nuclear secondary stages) in an indeterminate state pending a senior-level government evaluation of their use in planetary defense against earthbound asteroids." In its FY2015 budget request, the NNSA noted that the nine-megaton B53 nuclear bomb, B53 component disassembly was "delayed", leading some observers to conclude they might be the warhead CSAs being retained for potential planetary defense purposes.Kinetic impact
 The impact of a massive object, such as a spacecraft or even another near-Earth object, is another possible solution to a pending NEO impact. An object with a high mass close to the Earth could be sent out into a collision course with the asteroid, knocking it off course.
When the asteroid is still far from the Earth, a means of deflecting the asteroid is to directly alter its momentum by colliding a spacecraft with the asteroid.
A
The impact of a massive object, such as a spacecraft or even another near-Earth object, is another possible solution to a pending NEO impact. An object with a high mass close to the Earth could be sent out into a collision course with the asteroid, knocking it off course.
When the asteroid is still far from the Earth, a means of deflecting the asteroid is to directly alter its momentum by colliding a spacecraft with the asteroid.
A NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
analysis of deflection alternatives, conducted in 2007, stated:
This deviation method, which has been implemented by DART and, for a completely different purpose (analysis of the structure and composition of a comet), by NASA's Deep Impact space probe, involves launching a spacecraft against the Near-Earth object, near Earth object. The speed of the asteroid is modified due to the law of conservation of momentum:
with V velocity of the spacecraft, V velocity of the celestial body before impact, and V the velocity after impact. M and M respective mass of the spacecraft and of the celestial body. Velocities are Vector space, vectors here.
 The European Union's NEOShield-2 Mission is also primarily studying the Kinetic Impactor mitigation method. The principle of the kinetic impactor mitigation method is that the NEO or Asteroid is deflected following an impact from an impactor spacecraft. The principle of momentum transfer is used, as the impactor crashes into the NEO at a very high velocity of or more. The momentum of the impactor is transferred to the NEO, causing a change in velocity and therefore making it deviate from its course slightly.
As of mid-2021, the modified AIDA (mission), AIDA mission has been approved. The NASA Double Asteroid Redirection Test (''DART'') kinetic impactor spacecraft was launched in November 2021. The goal was to impact
The European Union's NEOShield-2 Mission is also primarily studying the Kinetic Impactor mitigation method. The principle of the kinetic impactor mitigation method is that the NEO or Asteroid is deflected following an impact from an impactor spacecraft. The principle of momentum transfer is used, as the impactor crashes into the NEO at a very high velocity of or more. The momentum of the impactor is transferred to the NEO, causing a change in velocity and therefore making it deviate from its course slightly.
As of mid-2021, the modified AIDA (mission), AIDA mission has been approved. The NASA Double Asteroid Redirection Test (''DART'') kinetic impactor spacecraft was launched in November 2021. The goal was to impact Dimorphos
(65803) Didymos I Dimorphos (provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a minor-planet moon of the near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a binary system. It has a diameter of and has been characterised as a low-density rubb ...
(nicknamed ''Didymoon''), the minor-planet moon of near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos. The impact occurred in September 2022 when Didymos is relatively close to Earth, allowing Earth-based telescopes and planetary radar to observe the event. The result of the impact will be to change the orbital velocity and hence orbital period of Dimorphos, by a large enough amount that it can be measured from Earth. This will show for the first time that it is possible to change the orbit of a small asteroid, around the size most likely to require active mitigation in the future. The second part of the AIDA (mission), AIDA missionthe ESA Hera (spacecraft), HERA spacecrafthas been approved by ESA member states in October 2019. It would reach the Didymos system in 2026 and measure both the mass of Dimorphos and the precise effect of the impact on that body, allowing much better extrapolation of the AIDA (mission), AIDA mission to other targets.
Asteroid gravity tractor
Another alternative to explosive deflection is to move the asteroid slowly over time. A small but constant amount of thrust accumulates to deviate an object sufficiently from its course. Edward T. Lu and Stanley G. Love have proposed using a massive unmanned spacecraft hovering over an asteroid to gravitationally pull the asteroid into a non-threatening orbit. Though both objects are gravitationally pulled towards each other, the spacecraft can counter the force towards the asteroid by, for example, an nuclear electric rocket, ion thruster, so the net effect would be that the asteroid is accelerated towards the spacecraft and thus slightly deflected from its orbit. While slow, this method has the advantage of working irrespective of the asteroid's composition or spin rate;rubble pile
In astronomy, a rubble pile is a celestial body that is not a monolith, consisting instead of numerous pieces of rock that have coalesced under the influence of gravity. Rubble piles have low density because there are large cavities between the ...
asteroids would be difficult to deflect by means of nuclear detonations, while a pushing device would be difficult or inefficient to mount on a fast-rotating asteroid. A gravity tractor would likely have to spend several years beside the asteroid to be effective.
A NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
analysis of deflection alternatives, conducted in 2007, stated:
Ion beam shepherd
Another "contactless" asteroid deflection technique has been proposed by C. Bombardelli and J. Peláez from the Technical University of Madrid. The method involves the use of a low-divergence ion thruster pointed at the asteroid from a nearby hovering spacecraft. The momentum transmitted by the ions reaching the asteroid surface produces a slow but continuous force that can deflect the asteroid in a similar way as the gravity tractor, but with a lighter spacecraft.Focused solar energy
H. Jay Melosh, H. J. Melosh with I. V. Nemchinov proposed deflecting an asteroid or comet by focusing solar energy onto its surface to create thrust from the resulting vaporization of material. This method would first require the construction of a space station with a system of large collecting, concave mirrors similar to those used in solar furnaces. Orbit mitigation with highly concentrated sunlight is scalable to achieving the predetermined deflection within a year even for a global-threatening body without prolonged warning time. Such a hastened strategy may become topical in the case of late detection of a potential hazard, and also, if required, in providing the possibility for some additional action. Conventional concave reflectors are practically inapplicable to the high-concentrating geometry in the case of a giant shadowing space target, which is located in front of the mirrored surface. This is primarily because of the dramatic spread of the mirrors' focal points on the target due to the optical aberration when the optical axis is not aligned with the Sun. On the other hand, the positioning of any collector at a distance to the target much larger than its size does not yield the required concentration level (and therefore temperature) due to the natural divergence of the sunrays. Such principal restrictions are inevitably at any location regarding the asteroid of one or many unshaded forward-reflecting collectors. Also, in the case of secondary mirrors use, similar to the ones found in Cassegrain reflector, Cassegrain telescopes, would be prone to heat damage by partially concentrated sunlight from primary mirror. In order to remove the above restrictions, V.P. Vasylyev proposed to apply an alternative design of a mirrored collector – the ring-array concentrator. This type of collector has an underside lens-like position of its focal area that avoids shadowing of the collector by the target and minimizes the risk of its coating by ejected debris. Provided the sunlight concentration ~ 5 × 103 times, a surface irradiance of around 4-5 MW/m2 leads to a thrusting effect ~ 103 N. Intensive ablation of the rotating asteroid surface under the focal spot will lead to the appearance of a deep "canyon", which can contribute to the formation of the escaping gas flow into a jet-like one. This may be sufficient to deflect a 0.5-km asteroid within several months and no addition warning period, only using ring-array collector size ~ 0.5 of asteroid diameter. For such a prompt deflection of the larger NEOs, 1.3-2.2 km, the required collector sizes are comparable to the target diameter. In the case of a longer warning time, the required size of the collector may be significantly decreased.
Mass driver
A mass driver is an (automated) system on the asteroid to eject material into space, thus giving the object a slow steady push and decreasing its mass. A mass driver is designed to work as a very low specific impulse system, which in general uses a lot of propellant, but very little power. The idea is that when using local material as propellant, the amount of propellant is not as important as the amount of power, which is likely to be limited.Conventional rocket engine
Attaching any spacecraft propulsion device would have a similar effect of giving a push, possibly forcing the asteroid onto a trajectory that takes it away from Earth. An in-space rocket engine that is capable of imparting an impulse of 106 N·s (E.g. adding 1 km/s to a 1000 kg vehicle), will have a relatively small effect on a relatively small asteroid that has a mass of roughly a million times more. Chapman, Durda, and Gold's white paper calculates deflections using existing chemical rockets delivered to the asteroid. Such direct force rocket engines are typically proposed to use highly-efficient electrically powered spacecraft propulsion, such as ion thrusters or VASIMR.Asteroid laser ablation
Similar to the effects of a nuclear device, it is thought possible to focus sufficient laser energy on the surface of an asteroid to cause flash vaporization / ablation to create either in impulse or to ablate away the asteroid mass. This concept, called asteroid laser ablation was articulated in the 1995 SpaceCast 2020 white paper "Preparing for Planetary Defense", and the 1996 Air Force 2025 white paper "Planetary Defense: Catastrophic Health Insurance for Planet Earth". Early publications include C. R. Phipps "ORION" concept from 1996, Colonel Jonathan W. Campbell's 2000 monograph "Using Lasers in Space: Laser Orbital Debris Removal and Asteroid Deflection", and NASA's 2005 concept Comet Asteroid Protection System (CAPS). Typically such systems require a significant amount of power, such as would be available from a Space-based solar power, Space-Based Solar Power Satellite. Another proposal is the Phillip Lubin's DE-STAR proposal: * The Directed Energy System for Targeting of Asteroids and ExplorRation, DE-STAR project, proposed by researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara, is a concept modular solar powered 1 µm, near infrared wavelength, laser array. The design calls for the array to eventually be approximately 1 km squared in size, with the modular design meaning that it could be launched in increments and assembled in space. In its early stages as a small array it could deal with smaller targets, assist solar sail probes and would also be useful in cleaning up space debris.Other proposals
* Wrapping the asteroid in a sheet of reflective plastic such as metallized polyethylene terephthalate, aluminized PET film as a solar sail * "Painting" or dusting the object with titanium dioxide (white) to alter its trajectory via increased reflected radiation pressure or with soot (black) to alter its trajectory via the Yarkovsky effect. * planetary science, Planetary scientist Eugene Shoemaker in 1996 proposed deflecting a potential impactor by releasing a cloud of steam in the path of the object, hopefully gently slowing it. Nick Szabo in 1990 sketched a similar idea, "cometary aerobraking", the targeting of a comet or ice construct at an asteroid, then vaporizing the ice with nuclear explosives to form a temporary atmosphere in the path of the asteroid. * Coherent digger array multiple 1-ton flat tractors able to dig and expel asteroid soil mass as a coherent fountain array, coordinated fountain activity may propel and deflect over years. * Attaching a tether and ballast mass to the asteroid to alter its trajectory by changing its center of mass. * Explosively pumped flux compression generator, Magnetic flux compression to magnetically brake and or capture objects that contain a high percentage of meteoric iron by deploying a wide coil of wire in its orbital path and when it passes through, Inductance creates an electromagnet solenoid to be generated.Deflection technology concerns
Carl Sagan, in his book Pale Blue Dot (book), ''Pale Blue Dot'', expressed concern about deflection technology, noting that any method capable of deflecting impactors ''away'' from Earth could also be abused to divert non-threatening bodies ''toward'' the planet. Considering the history of genocidal political leaders and the possibility of the bureaucratic obscuring of any such project's true goals to most of its scientific participants, he judged the Earth at greater risk from a man-made impact than a natural one. Sagan instead suggested that deflection technology be developed only in an actual emergency situation. All low-energy delivery deflection technologies have inherent fine control and steering capability, making it possible to add just the right amount of energy to steer List of asteroid close approaches to Earth, an asteroid originally destined for a mere close approach toward a specific Earth target. According to former NASA astronaut Rusty Schweickart, the gravitational tractor method is controversial because, during the process of changing an asteroid's trajectory, the point on the Earth where it could most likely hit would be slowly shifted across different countries. Thus, the threat for the entire planet would be minimized at the cost of some specific states' security. In Schweickart's opinion, choosing the way the asteroid should be "dragged" would be a tough diplomatic decision. Analysis of the uncertainty involved in nuclear deflection shows that the ability to protect the planet does not imply the ability to target the planet. A nuclear explosion that changes an asteroid's velocity by 10 meters/second (plus or minus 20%) would be adequate to push it out of an Earth-impacting orbit. However, if the uncertainty of the velocity change was more than a few percent, there would be no chance of directing the asteroid to a particular target.Planetary defense timeline
 * In their 1964 book, ''Islands in Space'', Dandridge M. Cole and Donald W. Cox noted the dangers of planetoid impacts, both those occurring naturally and those that might be brought about with hostile intent. They argued for cataloging the minor planets and developing the technologies to land on, deflect, or even capture planetoids.
* In 1967, students in the Aeronautics and Astronautics department at MIT did a design study, "Project Icarus", of a mission to prevent a hypothetical impact on Earth by asteroid 1566 Icarus. The design project was later published in a book by the MIT Press and received considerable publicity, for the first time bringing asteroid impact into the public eye.
* In the 1980s NASA studied evidence of past strikes on planet Earth, and the risk of this happening at the current level of civilization. This led to a program that maps objects in the Solar System that both cross Earth's orbit and are large enough to cause serious damage if they hit.
* In the 1990s, US Congress held hearings to consider the risks and what needed to be done about them. This led to a US$3 million annual budget for programs like
* In their 1964 book, ''Islands in Space'', Dandridge M. Cole and Donald W. Cox noted the dangers of planetoid impacts, both those occurring naturally and those that might be brought about with hostile intent. They argued for cataloging the minor planets and developing the technologies to land on, deflect, or even capture planetoids.
* In 1967, students in the Aeronautics and Astronautics department at MIT did a design study, "Project Icarus", of a mission to prevent a hypothetical impact on Earth by asteroid 1566 Icarus. The design project was later published in a book by the MIT Press and received considerable publicity, for the first time bringing asteroid impact into the public eye.
* In the 1980s NASA studied evidence of past strikes on planet Earth, and the risk of this happening at the current level of civilization. This led to a program that maps objects in the Solar System that both cross Earth's orbit and are large enough to cause serious damage if they hit.
* In the 1990s, US Congress held hearings to consider the risks and what needed to be done about them. This led to a US$3 million annual budget for programs like Spaceguard
The term Spaceguard loosely refers to a number of efforts to discover, catalogue, and study near-Earth objects (NEO), especially those that may impact Earth ( potentially hazardous objects).
Asteroids are discovered by telescopes which repeate ...
and the near-Earth object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). ...
program, as managed by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
and USAF.
* In 2005 a number of astronauts published an open letter through the Association of Space Explorers calling for a united push to develop strategies to protect Earth from the risk of a cosmic collision.
* It is currently (as of late 2007) estimated that there are approximately 20,000 objects capable of crossing Earth's orbit and large enough (140 meters or larger) to warrant concern. On the average, one of these will collide with Earth every 5,000 years, unless preventive measures are undertaken. It was anticipated that by year 2008, 90% of such objects that are 1 km or more in diameter will have been identified and will be monitored. The further task of identifying and monitoring all such objects of 140m or greater was expected to be complete around 2020. By April 2018, astronomers have spotted more than 8,000 near-Earth asteroids that are at least 460 feet (140 meters) wide and it is estimated about 17,000 such near-Earth asteroids remain undetected. By 2019, the number of discovered near-Earth asteroids of all sizes totaled more than 19,000. An average of 30 new discoveries are added each week.
* The Catalina Sky Survey
Catalina Sky Survey (CSS; obs. code: 703) is an astronomical survey to discover comets and asteroids. It is conducted at the Steward Observatory's Catalina Station, located near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States.
CSS focuses on the search ...
(CSS) is one of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's four funded surveys to carry out a 1998 U.S. Congress mandate to find and catalog by the end of 2008, at least 90 percent of all near-Earth objects (NEOs) larger than 1 kilometer across. CSS discovered over 1150 NEOs in years 2005 to 2007. In doing this survey they discovered on November 20, 2007, an asteroid, designated 2007 WD5, , which initially was estimated to have a chance of hitting Mars on January 30, 2008, but further observations during the following weeks allowed NASA to rule out an impact. NASA estimated a near miss by .
* In January 2012, after a near pass-by of object 2012 BX34, a paper entitled "A Global Approach to Near-Earth Object Impact Threat Mitigation" was released by researchers from Russia, Germany, the United States, France, Britain, and Spain, which discusses the "NEOShield" project.
* In January 2022, The NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) is a robotic astronomical survey and early warning system optimized for detecting smaller near-Earth objects a few weeks to days before they impact Earth.
Funded by NASA, and developed an ...
(ATLAS)—a state-of-the-art asteroid detection system operated by the University of Hawaiʻi (UH) Institute for Astronomy (IfA) for the agency’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO)—has reached a new milestone by becoming the first survey capable of searching the entire dark sky every 24 hours for near-Earth objects (NEOs) that could pose a future impact hazard to Earth. Now comprising four telescopes, ATLAS has expanded its reach to the southern hemisphere from the two existing northern-hemisphere telescopes on Haleakalā and Maunaloa in Hawai’i to include two additional observatories in South Africa and Chile.
See also
* Asteroid impact prediction * Asteroid Redirect Mission * Asteroid Day * Asteroids in fiction *B612 Foundation
The B612 Foundation is a private nonprofit foundation headquartered in Mill Valley, California, United States, dedicated to planetary science and planetary defense against asteroids and other near-Earth object (NEO) impacts. It is led mainl ...
* Colonization of the Moon
* Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development
* Global catastrophic risk
* Gravity tractor
* Lost minor planet
* Near-Earth Asteroid Scout
* Near-Earth object
* Potentially hazardous object
* United States Space Force
Sources
References
Citations
General bibliography
* Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez et al. 1980 paper in ''Science'' magazine on the great mass extinction 65 million years ago that led to the proliferation of mammal species such as the rise of the human race, thanks to Impact event, asteroid-impact, a controversial theory in its day, now generally accepted. ** * Clark R. Chapman, Daniel D. Durda & Robert E. Gold (February 24, 2001) ''Impact Hazard, a Systems Approach'', white paper on public policy issues associated with the impact hazard, aboulder.swri.edu
* Donald W. Cox, and James H. Chestek. 1996. ''Doomsday Asteroid: Can We Survive?'' New York: Prometheus Books. . (Note that despite its sensationalist title, this is a good treatment of the subject and includes a nice discussion of the collateral space development possibilities.) * Izzo, D., Bourdoux, A., Walker, R. and Ongaro, F.; "Optimal Trajectories for the Impulsive Deflection of NEOs"; Paper IAC-05-C1.5.06, 56th International Astronautical Congress, Fukuoka, Japan, (October 2005). Later published in Acta Astronautica, Vol. 59, No. 1-5, pp. 294–300, April 2006, available i
esa.int – The first scientific paper proving that Apophis can be deflected by a small sized kinetic impactor.
* David Morrison
''Skeptical Inquirer'' 1997.
David Morrison, Alan W Harris, Geoff Summer, Clark R. Chapman, & Andrea Carusi ''Dealing with Impact Hazard'', 2002 technical summary
* Kunio M. Sayanagi
"How to Deflect an Asteroid"
''Ars Technica'' (April 2008). * Russell L. Schweickart, Edward T. Lu, Piet Hut and Clark R. Chapman; "The Asteroid Tugboat"; ''Scientific American'' (November 2003). Vol. 289, No. 5, pp. 54–61. .
Further reading
General * Air Force 2025.Planetary Defense: Social, Economic, and Political Implications
', United States Air Force, Air Force 2025 Final Report webpage, December 11, 1996. * Belton, M.J.S.
Mitigation of Hazardous Comets and Asteroids
', Cambridge University Press, 2004, * Bottke, William F.
Asteroids III
' (Space Science Series), University of Arizona space science series, University of Arizona Press, 2002, * Burrows, William E
''The Asteroid Threat: Defending Our Planet from Deadly Near-Earth Objects''
* Lewis, John S.
Comet and Asteroid Impact Hazards on a Populated Earth: Computer Modeling
' (Volume 1 of Comet and Asteroid Impact Hazards on a Populated Earth: Computer Modeling), Academic Press, 2000, * Marboe, Irmgard : ''Legal Aspects of Planetary Defence.'' Brill, Leiden 2021, ISBN 978-90-04-46759-0. * Schmidt, Nikola et al.: ''Planetary Defense: Global Collaboration for Defending Earth from Asteroids and Comets.'' Springer, Cham 2019, . * Verschuur, Gerrit L. (1997
''Impact!: The Threat of Comets and Asteroids''
Oxford University Press,
External links
"Deflecting Asteroids"
(with solar sails) by Gregory L. Matloff, ''IEEE Spectrum'', April 2012
Near Earth Objects Directory
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20100325002654/http://star.arm.ac.uk/impact-hazard/ Armagh University: Near Earth Object Impact Hazard ]
Threats from Space: A Review of U.S. Government Efforts to Track and Mitigate Asteroids and Meteors (Part I and Part II): Hearing before the Committee on Science, Space, and Technology, House of Representatives, One Hundred Thirteenth Congress, First Session, Tuesday, March 19, 2013 and Wednesday, April 10, 2013
{{DEFAULTSORT:Asteroid Impact Avoidance Planetary defense, * Asteroids Earth Future problems Impact events Prevention Space weapons